Understanding Prostate Enlargement: Symptoms, Causes and Natural Management
The prostate is a crucial gland, a part of the male reproductive system responsible for secreting the fluid that carries sperm during ejaculation. As men age, it is common for the prostate to grow larger, and the condition is known as prostate enlargement, which is medically called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Though the condition is associated with uncomfortable symptoms and affects the quality of life, it does not cause cancer or increase the risk of prostate cancer.
According to experts, the enlarged prostrate condition affects 5–6% of men aged 40 to 64 and 29–33% of those aged 65 and older. However, this condition rarely causes symptoms in men below 40 years of age.
Who is at risk of developing prostate enlargement?
The risk of enlarged prostrate is observed in individuals who are:
- Forty years and older
- Family history of BPH
- Have certain underlying conditions such as heart and blood vessel disease, type 2 diabetes, obesity, chronic kidney disease or erectile dysfunction.
- Individuals who are not physically active
Causes
The precise reason behind prostate enlargement is yet unknown. Ageing, modification of testicular cells and variations in testosterone levels may be potential causes. During early puberty, the size of the prostate gland doubles. Around the age of 25, it begins to grow again, and for most men, this continues throughout their lives.
Symptoms
In some cases, increased prostrate size can pressed against the wall of the urethra. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Inability to urinate (urinary retention)
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder
- Urinary incontinence
- Required to urinate two or more times per night
- Painful urination or bloody urine (which may indicate an infection)
- The start of the urinary stream is delayed or slowed.
- Straining to urinate
- Strong and sudden urge to urinate
In addition to the above symptoms, conditions such as urinary tract infections, inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis), bladder or kidney stones and nerve problems affecting the bladder can also cause symptoms.
Diagnosis
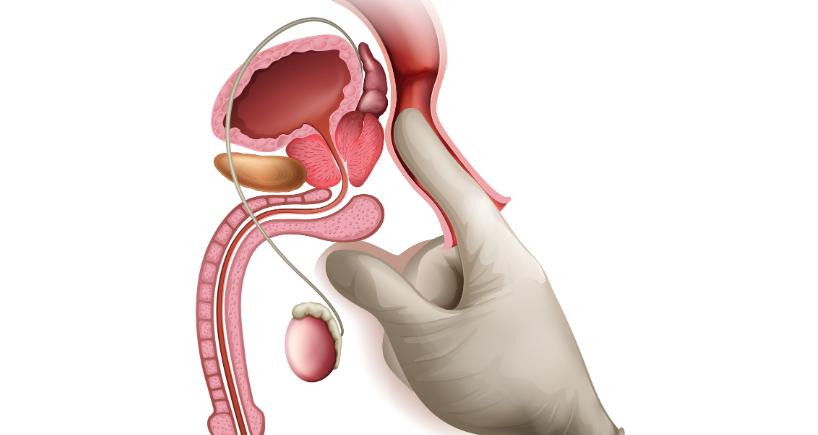
When you have symptoms, your healthcare provider will initially perform a physical examination which is conducted through digital rectal examination. In this procedure, the doctor wears a glove and gently inserts the finger into your rectum to assess the size and shape of the prostate. The doctor may advise another test, which includes:
- A blood test to determine kidney function and check for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. Higher PSA levels indicate an enlarged prostate
- Based on blood tests, the doctor may advise screening for prostate cancer
- A renal and bladder ultrasound scan
Treatment
The treatment of prostate enlargement is recommended based on the symptom severity and how much they affect your daily life. Treatment options include natural management, medicine and surgery.
Natural management
For mild symptoms, self-care steps can often be effective:
- Urinate when needed: Go to the bathroom as soon as you feel the urge and follow a timed schedule for nutrition.
- Avoid alcohol and caffeine drinks: Avoid these especially in the evening, as these can trigger symptoms.
- Manage fluid intake: Distribute the fluid consumption throughout the day. Avoid consuming any fluids within two hours before sleeping.
- Refrain from certain medicines: Avoid over-the-counter cold and sinus medicines containing decongestants and antihistamines. These medicines can worsen the symptoms.
- Stay warm and active: Cold weather and lack of physical activity can exacerbate symptoms.
- Minimise stress and anxiety: Nervousness and tension can lead to more frequent urination.
Medications
In case of severe symptoms, medications such as alpha-blockers, antibiotics or certain hormonal agents are recommended to control the symptoms.
Surgery
Surgery may be recommended for severe symptoms that are not controlled by self-care or medications or complications, such as:
- Recurrent blood in urine
- Bladder stones
- Urinary retention
- Urinary incontinence
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms, including the size and shape of the prostate gland. Regular assessment is necessary to monitor symptoms and adjust the treatment.